
This one is blue. Interesting cover, but not nearly as cool as the Basic Set. It’s okay, but nothing too impressive.
In the original Box Set, this book came bundled with the module X1: Isle of Dread, also written by Cook, and which is probably one of the most highly regarded adventures ever made. I might perhaps cover this after the Expert Set is done. (Because it is indeed very good, but also very unlike any other modern modules.)
The first page is a number of tables from the Basic Set, like the Ability Score modifiers, missile weapon ranges, and all the Encumbrance rules. The idea here seems to be that you have any tables you might need too look up during a game in a single book. Very thoughtful.
Part 1: Introduction
Obviously, this is an expansion to the Basic Set and assumes that you know how Basic works. The idea of reassembling the two books into one is mentioned again, but without printing all 128 pages (which I won’t) it’s hard to get an impression of how good that would actually look.
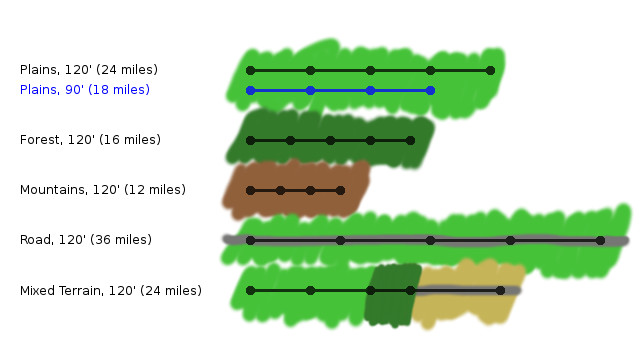
The Expert Set has rules for letting characters advance to 14th level, and includes new spells, magic items, monsters, and treasures for such higher level adventures. (Or lower levels when you go to dungeons.) There is also a big deal being made from going beyond dungeon adventures into wilderness adventures. “In expanding the campaign, the DM will create whole nations and cultures, giving the characters a history and background. Adventurers can even shape the hisoty of their world as they become more powerful.” We’re going to see how well the book delivers on this lofty promise later on.
At higher levels, players also may build strongholds for their characters and then become lords of their own territories.
A few new terms are introduced as well: A wilderness is any area that is outdoors. When characters reach 9th level, they have achieved name level, as by then a magic-user is called a “wizard” and a fighter a “Lord”, and their title won’t be changing any more after that. (At the lower levels, every class level comes with a fancy sounding title that doesn’t actually mean anything.) When characters build their own fortified base, it is called a castle when build by fighters, clerics, or wizards, a hideout when build by thieves, and a stronghold when build by demhumans.
A new concept introduced here are reversed spells, which allows spellcasters to cast their spells for the opposite effect they usually know. There is also magical research, which allows spellcasters to invent new spells and make magic items. “Many details of magical research are left the DM.” Interesting they already felt the need to mention that here in the introduction of the book.
There’s a historically very interesting paragraph on the second page of the introduction. At least if you have an interest in early D&D and the nerdiest aspects of OSR.
Most important, the characters in the wilderness campaign do not exist in a vacuum. The DM should have events going on elsewhere that may affect (or be affected by) the actions of the players. There may be any number of “plots” going on at once, and the DM should try to involve each player in some chain of events. These should develop logically from the actions of those involved. It is important not to force the action to a pre-determined conclusion. The plot lines can always be adjusted for the actions of the players.
This could very well be argued to be official definition of what is now usually called Sandbox campaigns. You could write small books about this quote alone. (And I am pretty sure someone did.) I won’t go into that here in great detail as there is plenty of more immediate stuff, but it’s interesting to see that Cook was stressing some points about open world campaigns that are still the source of great debate 35 years later.
Since player characters die with considerable frequency and the default assumption is that all new characters are created at 1st level, “As a guideline, not a rule, it is suggested that characters who have a difference in levels of 5 or greater” should not play in the same adventures. The reason for that being that a 1st level character in a 6th level party would not have any realistic chance of surviving anything the party might run into and that a 12th level character in a 6th level party would simply clear out all obstacles by himself, reducing the other characters to supporting spectators. Still, I can imagine a great number of 3rd edition players considering even a 5 level difference an outrage and a travesty.
The suggestion that a 3rd level character and an 8th level character should probably play in different adventures seems strange though. This seems based on the assumption that D&D is played in wargaming clubs where there are plenty of different games run by different groups. However, the Basic Set explicitly mentioned that B/X is meant to make D&D accessible to people beyond this original crowd, so it seems a bit out of place. The obvious alternative solution would be to have new characters created 5 levels below the highest level character in the party.
There’s also a couple of extra notes for people who want to use the Expert Set with the older Holmes Basic rules. I know nothing about that one, but I assume the Expert Set would indeed have everything needed to do that. The only thing it’s really missing are combat rules, monsters, and spells, which the Holmes Basic set most likely already had in a very similar form. Continue reading “Reading through Cook Expert (1981)”




 Only on a roll of 2 on a 2d6 does a reaction roll actually indicate an immediate attack and a 3 to 5 indicates hostility with a chance that the creatures might attack. This results in only a 28% chance that a fight breaks out without the players initiating it. If you start making reaction rolls for any encounter where the reaction isn’t automatically fixed, it will change the game quite a lot. Orcs and ogres are no longer monsters but people just like bndits, mercenaries, or barbarians. Their culture might be different and unappealing to many of the PCs, but if the players handle it right they can be interacted with just like people.
Only on a roll of 2 on a 2d6 does a reaction roll actually indicate an immediate attack and a 3 to 5 indicates hostility with a chance that the creatures might attack. This results in only a 28% chance that a fight breaks out without the players initiating it. If you start making reaction rolls for any encounter where the reaction isn’t automatically fixed, it will change the game quite a lot. Orcs and ogres are no longer monsters but people just like bndits, mercenaries, or barbarians. Their culture might be different and unappealing to many of the PCs, but if the players handle it right they can be interacted with just like people. This came as a bit of a surprise to me. Even though they are all D&D, there’s a huge number of major differences between the various editions. The most common reason I’ve seen discussed for 3rd edition being bad at high level play is that wizards got more spells per day and lost most of the limitations and weaknesses they had in AD&D. But that alone can’t be reason if the problem goes back all the way to the mid 70s.
This came as a bit of a surprise to me. Even though they are all D&D, there’s a huge number of major differences between the various editions. The most common reason I’ve seen discussed for 3rd edition being bad at high level play is that wizards got more spells per day and lost most of the limitations and weaknesses they had in AD&D. But that alone can’t be reason if the problem goes back all the way to the mid 70s.