Looking over my older posts, I’ve started talking about Barbarians of Lemuria some five years back, and been thinking about how to combine elements of it with aspects of Apocalypse World basically since I first learned about that game two years ago. Both are pretty rules light, and while they are both presented with quite distinctive settings, the mechanics have always struck me as having great potential for a very wide range of campaigns. They are both rules systems that have mechanics to figure out the outcome of uncertain situations when the PCs try to do something in the face of opposition from other people or the environment, which they do quick and painlessly and then are out of your hair to let you go on with the developing story. I really like this approach to what an RPG should be and do.
Some kind of hybrid of the two games has long been a vision of an ideal game for me, but since I have little personal experience with both BoL and AW, cobbling something entirely new together never seemed like a real option. And the way my groups form, getting a number of players together to play the weird homebrew system of a GM they never played with never really had any promise of success.
When I was looking into fantasy games based on the mechanics of Apocalypse World, there were really only two that have any popular presence. The first of course being Dungeon World, which I found to be very disappointing as it is an attempt to recreate the experience of D&D adventures with different dice rolling mechanics instead of doing anything with the very different approach to what a campaign can be that is promised by the Apocalypse World rules. And the other one is Blades in the Dark.
 This game had been recommended to me by some people in the past and I had taken a look at it some time back. I don’t recall what I had been looking for back then when I took a peek, but I remember that I mostly looked at the setting, which is very post-apocalyptic Victorian steampunk. It’s basically Thief and Dishonored the Roleplaying Game, which really is cool, but at the time made me write it off as not being useful to whatever I was trying to do. I also remember seeing it has only three attributes, which made me go eww… Which turns out was a real shame.
This game had been recommended to me by some people in the past and I had taken a look at it some time back. I don’t recall what I had been looking for back then when I took a peek, but I remember that I mostly looked at the setting, which is very post-apocalyptic Victorian steampunk. It’s basically Thief and Dishonored the Roleplaying Game, which really is cool, but at the time made me write it off as not being useful to whatever I was trying to do. I also remember seeing it has only three attributes, which made me go eww… Which turns out was a real shame.
Because looking at the system again from a mechanics focused perspective, it really strikes me as the closest thing I have yet encountered to that idealized blend of Barbarians of Lemuria and Apocalypse World, I had been dreaming of. It’s of course not exactly the game that I want to run for my next Kaendor campaign. There are all kinds of peripheral rules in this game about the gang of the PC’s increasing their reputation in the underworld, fighting for turf, and dealing with the police putting pressure on their activities, which really wouldn’t have any place in my campaign. But the core mechanics for making characters, character advancement, task resolution, and character durability is really solid.
While it’s not necessarily being more compact than Apocalypse World, it is much more straightforward and easy to grasp, even though at first there seem to be a lot of new mechanical concepts and principles you have to dig through. And Blades in the Dark really is quite a big book that doesn’t scream rules light. But I tried to write down the basics of character creation and action resolution as a simple introductory handout for new players, and I managed to get it all on only two and a half pages. (Excluding the rules for running a criminal empire.) That’s really quite impressive.
The Basics of the System
Characters in Blades in the Dark are really very simple. They mostly come down to 12 action ratings and 3 derived attributes. But these are not like attributes and skills like you see them in most other skill based systems, where you add your attribute scores to your skill rank to determine what dice you roll. Instead you have twelve basic actions, which in other games would be skills, or moves in Apocalypse World. Anything that PCs might do that has a chance of failure and negative consequences falls under one of these twelve actions.
- Attune (do magic stuff)
- Command (order people around)
- Consort (chat with people)
- Finesse (climbing, jumping, picking pockets, …)
- Hunt (tracking, trapping, …)
- Prowl (sneaking)
- Skirmish (fighting)
- Study (inspect or research a thing or person)
- Survey (observe people or places)
- Sway (convince people of things)
- Tinker (work with machines)
- Wreck (break stuff)
These actions are not methods or techniques, but arranged by outcomes. Skirmish is the action for the vast majority of ways that you can fight, regardless of weapons, armor, fighting style, and so on. Sway can be debating, deceiving, seducing, pleading, or whatever else you can think of to make people change their mind with your words. I can’t really think of anything to do with Prowl other than sneaking past people without being detected, and Study and Survey do overlap quite a bit, but I can’t really think of anything that might come up in a game where you need any other category of action as a player. Characters have a rating for all these actions that goes from 0 to 4.
What I really like is that there are twelve equal actions and only one of them is combat. Hunt and Wreck can also be used for violence in some situation, but that’s not their primary purpose. Treating fighting as equal to all other actions is something that really appeals to me and makes it a very inviting system for games where fighting is not the main event of adventures.
Unlike Apocalypse World, where you always roll 2d6 and add your attribute score to the result, Blades in the Dark has you roll a number of d6 that is equal to your rating, plus and minus additional dice for various circumstances. (If you end up with less than 1 die, you roll 2 dice and take the lower one.) The die with the highest number is your result for the roll, with a 6 being a success, a 4 or 5 giving you a success but also negative consequences, and 1 to 3 being only the bad consequences with no success. I’m not generally a fan of dice pools, but picking the highest number out of only up to 6 or 7 dice at the most with no additions is really quick and painless.
While there are attributes, they are not very similar to attributes in other games. Instead the 12 action ratings are grouped into three groups of four, resulting in four Insight actions, four Prowess actions, and four Resolve actions. The attribute score is simply the number of actions for which you have a rating of 1 or higher, resulting in a score of 0 to 4, which increases over time as you put a first point into the skills of that group. Attributes are mostly used when you roll to reduce the severity of negative consequences from a failed or partially successful action roll, and for tracking which action ratings you can improve when you get XP.
Characters also start with 1 special ability selected from a long list of options, and probably gain a new one that can also be freely selected every 1 to 3 game sessions.
And that is mostly it. There are of course a lot more bells and whistles regarding items, wealth, the injury and stress mechanic, but attributes and special abilities are more or less all the character creation and character advancement for this game.
Action Resolution
Taking an action in Blades in the Dark work the following way.
- The player describes what his character is trying to do.
- The player declares which of his character’s action ratings he will use for the roll.
- The GM judges the positioning for the action, which is the potential severity of the consequences should the action roll fail or only be a partial success.
- The GM judges the effect if the roll will be a success. Based on the approach the player described, the GM decides if it should result in the ordinary outcome for such an action, or the result will be of limited or greater magnitude.
- The player can decide to push himself to get an extra die for the roll, and another player can decide to assist and also add an additional die.
Basically this come down to what happens in most games with a GM who isn’t a jerk. The player ask “Could it work if I…” and the GM replies “Yes, but the chance is…”. Then the player might take it and make the roll, but could also decide that he really wants a greater effect than the GM declared and change the action to something more daring that also results in a worse positioning by increasing the danger resulting from a failure. Or the other way around, the player might decide that the danger is too high and instead change the action to something with a better positioning and accepting a reduced effect.
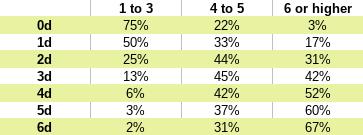
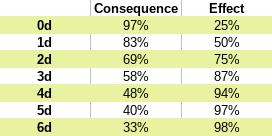
To keep things simple, there are only three categories of position: Controlled, Risky, and Desperate. And only three categories of effect: Limited, standard, and greater. This is easy to follow without any math involved. Do you want risk high or low danger and do you want to go for high or low reward? It’s not always a simple trade-off. Sometimes things are so much in your favor that you only have the low risk of controlled positioning and the expectation of a greater effect as the outcome. Or things look extremely bleak and you can only expect a lesser effect even though the positioning is desperate.
But these things don’t come down to only luck. Players have quite a lot of room to control the damage a failed action roll leads to. At any time, a player can declare that the severity of an injury or complication resulting from a roll is reduced by one category. The GM can say “You fall from the roof and badly hurt your leg. Is it broken?” And the player can decide to reduce the damage and say “No, fortunately it just seems sprained.” You can always do this, but it comes at the expanse of added stress. And when a character reaches 10 stress during an adventure, the character has some kind of mental breakdown that takes him out of the adventure and leaves a permanent mark on his mind. You also gain stress when pushing yourself or assisting another character to add additional dice to an action roll. Stress can also result from exposure to the supernatural, just like it does in Darkest Dungeon. Injuries will heal, but damage to the mind sticks around. So you might not always want to reduce the severity of your injuries or complications.
Forged in the Dark
The really neat thing that I found out today is that there is an SRD for the system that contains most of the rules that are not specific to the Duskwall setting of Blades in the Dark. It does not include the seven playbooks (character templates in PtBA games), but simply has all the special abilities put into a big single list from which GMs can put together their own lists for different character archetypes in their campaign. The SRD even has a template to make your own playbooks, and I think it has everything you need to fully recreate the ones from BitD. (Not sure what difference it makes, but there surely must be some copyright considerations behind this.) The only other thing from outside the setting chapter I’ve found to be not included are the four types of undead in Duskwall, but again the mechanics for making your own are there.
There also is of course a license to make your own stuff with the material from the SRD and using the Forged in the Dark label for it. The License is extremely generous and only requires you to include an attribution to John Harper and One Seven Design and not claim any official connection or endorsement by them. The Duskwall setting remains copyrighted, but everything in the SRD is fair game. And that’s all there is. Which I think is really cool.
Nothing set in stone yet, but right now I really want to give this a try for my next campaign. Aside from the criminal empire rules, this seems like a really well rounded system not just for fantasy but in general, and I think you could run a campaign even with just the basics. I can absolutely see myself making up some new rules for paranormal investigation, but I don’t think that’s even necessary to start a campaign. Really looking forward to trying this out.
 If you are familiar with Apocalypse World, then The Sprawl immediately shows that it’s a very close descendant. There are of course many different games that use the underlying dice mechanic and principles of Apocalypse World, but this game is much closer to the first game that started it all than for example Dungeon World or Blades in the Dark. The Sprawl is the first other game I’ve seen that retains most of the basic moves from Apocalypse World mostly as they are. The names have been changed to a style that (the author assumes) have a more cyberpunk feel, but you still have the Go Aggro and Seize by Force moves that make conflict scenes in Apocalypse World so unique. The playbooks for different character types are all completely different from those in Apocalypse World, and while I think the Hardholder and Chopper could have been really fun in a cyberpunk setting, the ten playbooks of The Sprawl really cover all the character archetypes you could ask for in a cyberpunk game very well.
If you are familiar with Apocalypse World, then The Sprawl immediately shows that it’s a very close descendant. There are of course many different games that use the underlying dice mechanic and principles of Apocalypse World, but this game is much closer to the first game that started it all than for example Dungeon World or Blades in the Dark. The Sprawl is the first other game I’ve seen that retains most of the basic moves from Apocalypse World mostly as they are. The names have been changed to a style that (the author assumes) have a more cyberpunk feel, but you still have the Go Aggro and Seize by Force moves that make conflict scenes in Apocalypse World so unique. The playbooks for different character types are all completely different from those in Apocalypse World, and while I think the Hardholder and Chopper could have been really fun in a cyberpunk setting, the ten playbooks of The Sprawl really cover all the character archetypes you could ask for in a cyberpunk game very well.